Also important for fetal brain development are omega 3 fatty acids. Basically the cranium consists of two parts.
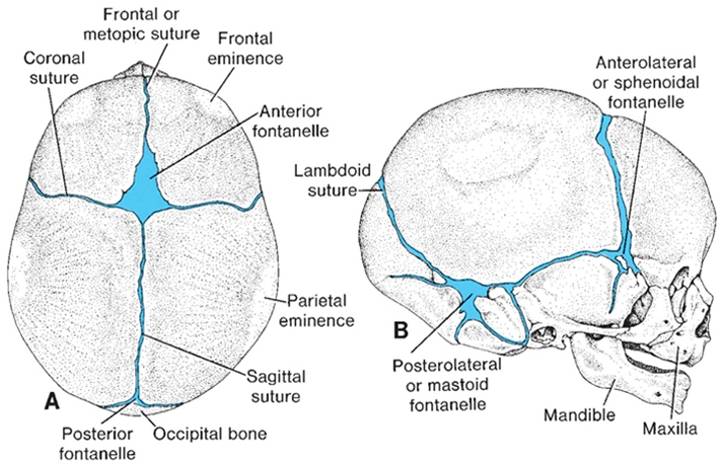 Development Of Skull Development Of Human Skeletal System
Development Of Skull Development Of Human Skeletal System
Craniosynostosis is often treated with surgery to reopen the fused area.
Skull development in fetus. In the first 2 images the bone cartilage is shown in blue and the new bone in red. This allows the amniotic fluid to reach these undeveloped organs in the womb. Craniosynostosis is a birth defect that involves the development of an infant s skull.
Hence there are no specific answers to the how s and why s of brain development. When this defect is present one or more of the soft spots in the skull close before they should. Although your baby s skull is soft and delicate it is designed to protect him during birth and help his expanding brain develop.
The brain has a high fat content and the omegas are helpful in the deposition of the fat in not only the brain but the eyes. Primary palate fusion in the human embryo between stage 17 and 18 from an epithelial seam to the mesenchymal bridge. Skull development in the womb early on in gestation baby s brain begins to form from the neural tube the larval stage of the central nervous system.
Development of the skull the skull cranium fig 7 develops from mesenchyme around the developing brain. However what does not change is the wonder of a cell an embryo that develops into a fetus then a child and finally an adult going through the passage of time and physical. The palate has two key stages of development during embryonic and an early fetal involving the fusion of structures epithelia to mesenchymal.
Cartilage at the dorsal end of the first arch meckel s cartilage. The brain and bones do not form properly as the neural tube fails to close during the initial weeks of fetal development. The images below show the combined endochondral and intramembranous ossification that is occurring in early fetal development week 12.
The cartilaginous skeleton of the first two pairs of the pharyngeal arch develop in to these part of the fetal cranium. This can cause pressure in the skull and in some cases impede brain development. Brain development in a fetus and its associated problems are still being researched.
She will continue to develop her brain cells throughout pregnancy and expand her functionality eventually being capable of regulating body temperature controlling her heartbeat and all other. This slow skull development is important for your child s healthy growth. Unlike an adult brain an infant s skull has joints that don t close up until later in childhood.