The pathophysiology of bipolar disorder or manic depressive illness mdi has not been determined and no objective biologic markers correspond definitively with the disease state. Characterized by episodes of severe mania and severe depression.
 Medical Conditions Causing Mania Or Mania Like Episodes Grepmed
Medical Conditions Causing Mania Or Mania Like Episodes Grepmed
Bipolar disorder and immune dysfunction.

Bipolar disorder pathophysiology. Epidemiological findings proposed pathophysiology and clinical implications brain sci. Bipolar disorder formerly called manic depression is a mental health condition that causes extreme mood swings that include emotional highs mania or hypomania and lows depression. Bipolar disorder sometimes is called manic depressive disorder or manic depression which are older terms.
We still don t know all the physical reasons involved in the development of bipolar disorder but fortunately scientists are continuing to learn new information all the time. Related journals of pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Authors joshua d rosenblat 1 2 roger s mcintyre 3 4 affiliations 1 department of psychiatry.
Understanding the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder is an ultimate goal of many scientists and clinicians but to date it remains poorly understood. Bipolar mood or affective disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of mania and depression in the same patient at different times. Bipolar disorder bipolar disorder also known as manic depressive illness is a brain disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood energy activity levels and the ability to carry out day to day tasks.
The bipolar disorder causes from biological differences neurotransmitters hormones and genetics. Types bipolar i. When you become depressed you may feel sad or hopeless and lose interest or pleasure in most activities.
Bipolar disorder is a chronic or episodic which means occurring occasionally and at irregular intervals mental disorder. Earlier known as manic depressive psychosis mdp 3. It can cause unusual often extreme and fluctuating changes in mood energy activity and concentration or focus.
Neurochemical factors in bipolar disorder bipolar disorder is primarily a biological disorder that occurs in a specific area of the brain and is due to the dysfunction of certain neurotransmitters.
 Molecular Neurobiology Of Bipolar Disorder A Disease Of Mood Stabilizing Neurons Trends In Neurosciences
Molecular Neurobiology Of Bipolar Disorder A Disease Of Mood Stabilizing Neurons Trends In Neurosciences
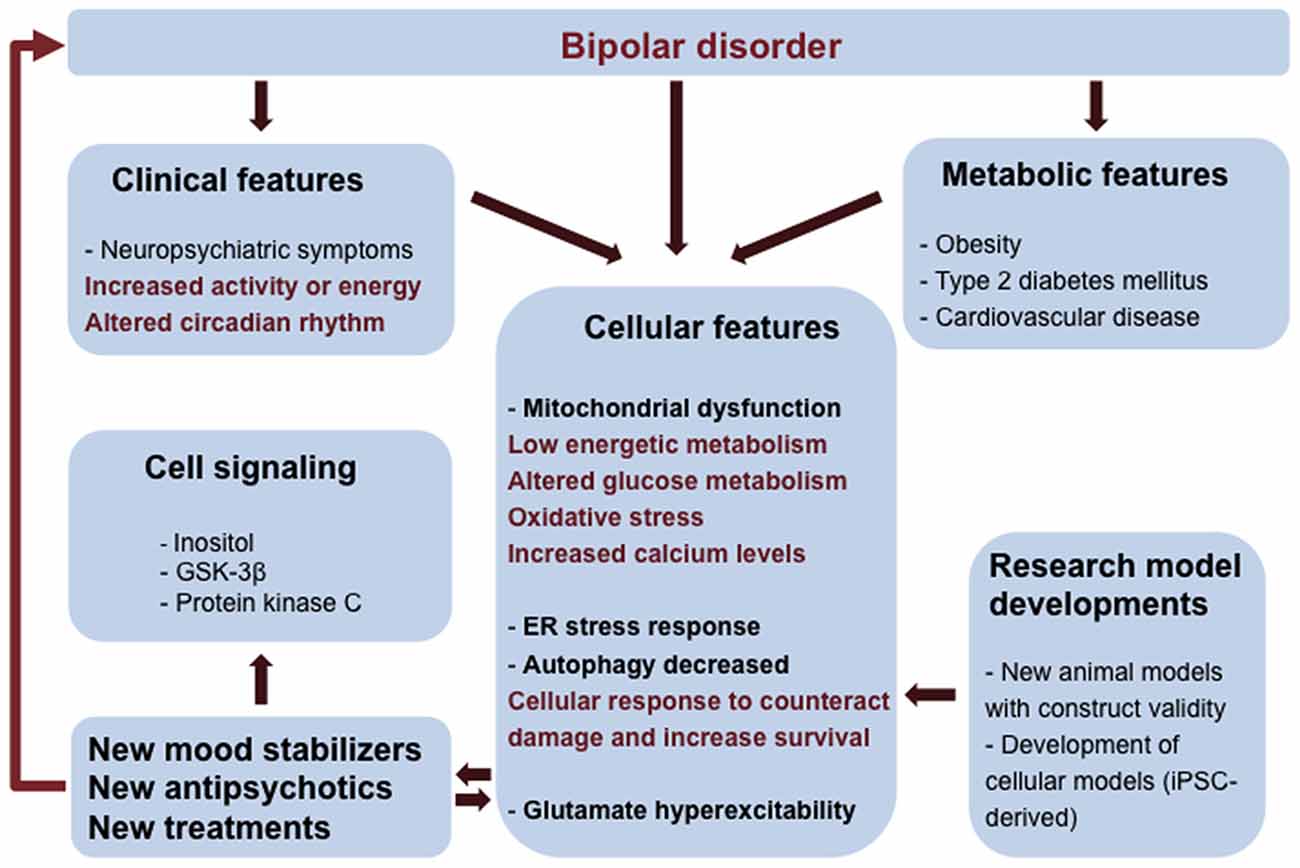 Frontiers Molecular Mechanisms Of Bipolar Disorder Progress Made And Future Challenges Cellular Neuroscience
Frontiers Molecular Mechanisms Of Bipolar Disorder Progress Made And Future Challenges Cellular Neuroscience
Bipolar Disorder Pathogenesis And Clinical Findings Calgary Guide
 The Role Of Neuroinflammation In Juvenile Bipolar Disorder
The Role Of Neuroinflammation In Juvenile Bipolar Disorder
 Pdf Update On Bipolar Disorder Biomarker Candidates
Pdf Update On Bipolar Disorder Biomarker Candidates
 The Integrative Model Of Bipolar Disorder Pathophysiology Dysfunctions Download Scientific Diagram
The Integrative Model Of Bipolar Disorder Pathophysiology Dysfunctions Download Scientific Diagram
 Pathophysiology In The Comorbidity Of Bipolar Disorder And Alzheimer S Disease Pharmacological And Stem Cell Approaches Sciencedirect
Pathophysiology In The Comorbidity Of Bipolar Disorder And Alzheimer S Disease Pharmacological And Stem Cell Approaches Sciencedirect
 Biological Hypotheses And Biomarkers Of Bipolar Disorder Sigitova 2017 Psychiatry And Clinical Neurosciences Wiley Online Library
Biological Hypotheses And Biomarkers Of Bipolar Disorder Sigitova 2017 Psychiatry And Clinical Neurosciences Wiley Online Library
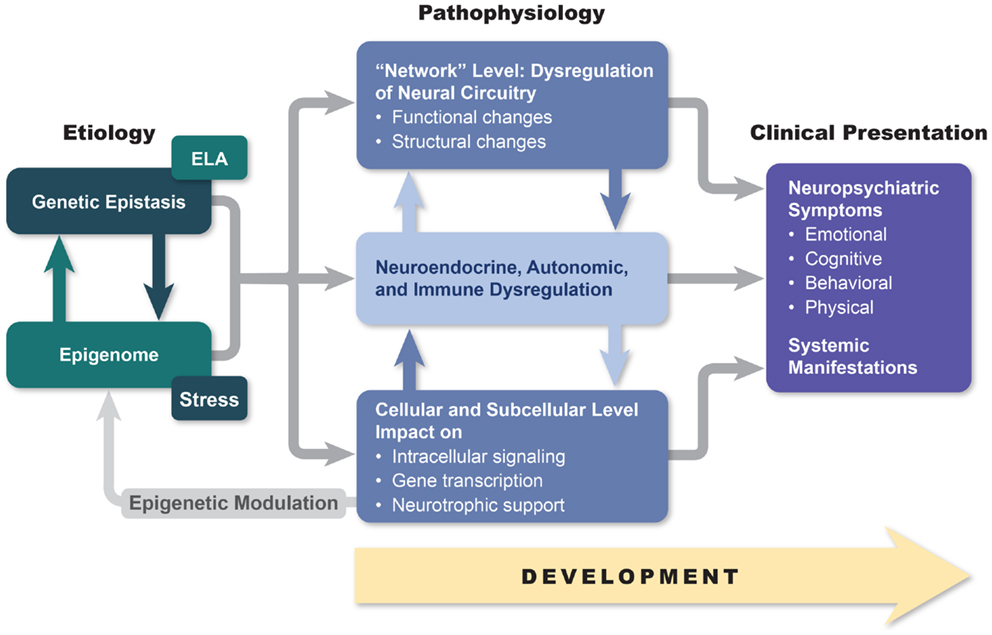 Frontiers Integrated Neurobiology Of Bipolar Disorder Psychiatry
Frontiers Integrated Neurobiology Of Bipolar Disorder Psychiatry
 A New Path Into Bipolar Disorder Comes To Light Eurekalert Science News
A New Path Into Bipolar Disorder Comes To Light Eurekalert Science News
 Figure 4 From Mixed States In Bipolar Disorder Etiology Pathogenesis And Treatment Semantic Scholar
Figure 4 From Mixed States In Bipolar Disorder Etiology Pathogenesis And Treatment Semantic Scholar
 Pdf Signaling Cellular Insights Into The Pathophysiology Of Bipolar Disorder Semantic Scholar
Pdf Signaling Cellular Insights Into The Pathophysiology Of Bipolar Disorder Semantic Scholar
 Signaling Cellular Insights Into The Pathophysiology Of Bipolar Disorder Sciencedirect
Signaling Cellular Insights Into The Pathophysiology Of Bipolar Disorder Sciencedirect
