Intracranial pressure icp is determined by the volume of brain parenchyma 80 blood 12 and csf 8 within a rigid cranial vault. Newborn 0 7 1 5mm hg infant 1 5 6 0 mm hg children 3 0 7 5 mmhg.
 Increased Intracranial Pressure Icp Nclex Review
Increased Intracranial Pressure Icp Nclex Review
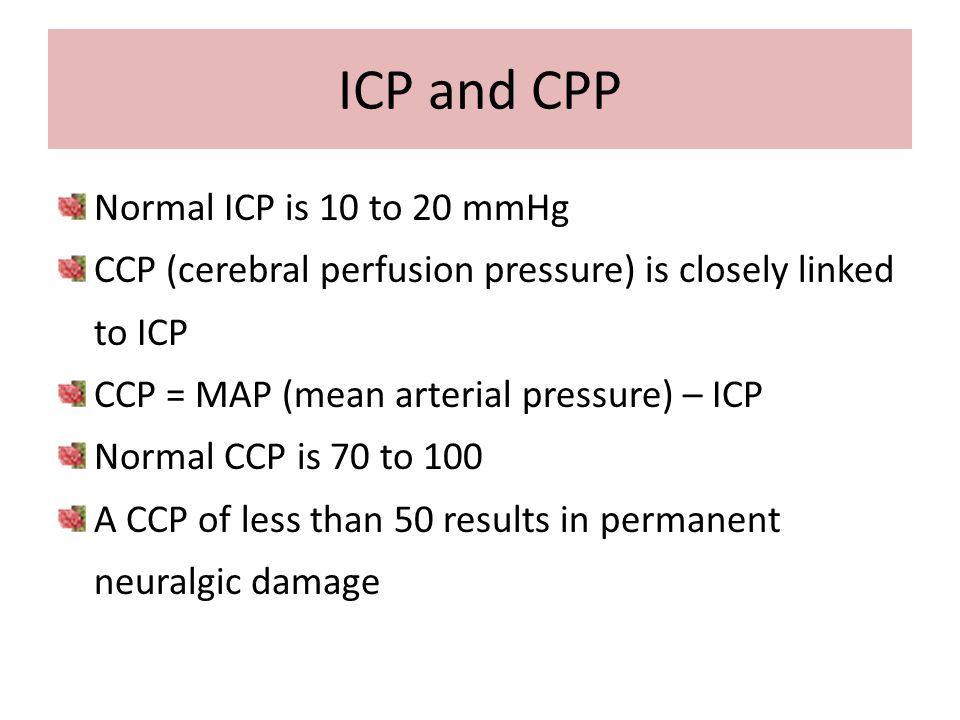
Normal cpp in pediatric patients is variable and dependent upon the age related map but should be at least 40 60 mmhg.
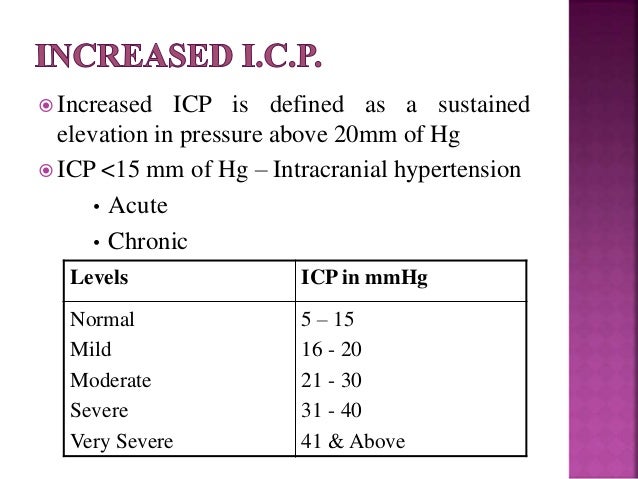
Normal icp levels. Marshall et al had suggested routine monitoring and aggressive maintenance of icp at less than 15 mm hg to improve the outcome based on favourable outcome of 77 as against 43 when icp was 15 mm hg. When icp is greater than 40mmhg there is almost always some neurological dysfunction impairment of consciousness problems breathing pupil dilation compression of brain found on mri as well as impairment of the brain s electrical activity an abnormal eeg. Icp normal adults 10 15 mm hg pediatric patients.
Patients with intracranial neoplasms can have baseline increases in intracranial pressures placing them at risk of cerebral herniation during valsalva or placement of neuraxial anesthesia stevenson and thompson 2005. A normal intracranial pressure is somewhere between 5 millimeters of mercury mmhg and 15 mmhg although normal icp levels vary by age. Any more than 20 mmhg and structures in the brain may begin to be impacted.
Intracranial pressure is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid inside the skull and on the brain tissue. Cerebral perfusion pressure cpp map icp. Because the cranial compartment is enclosed by a rigid skull it has a limited ability to accommodate additional volume.
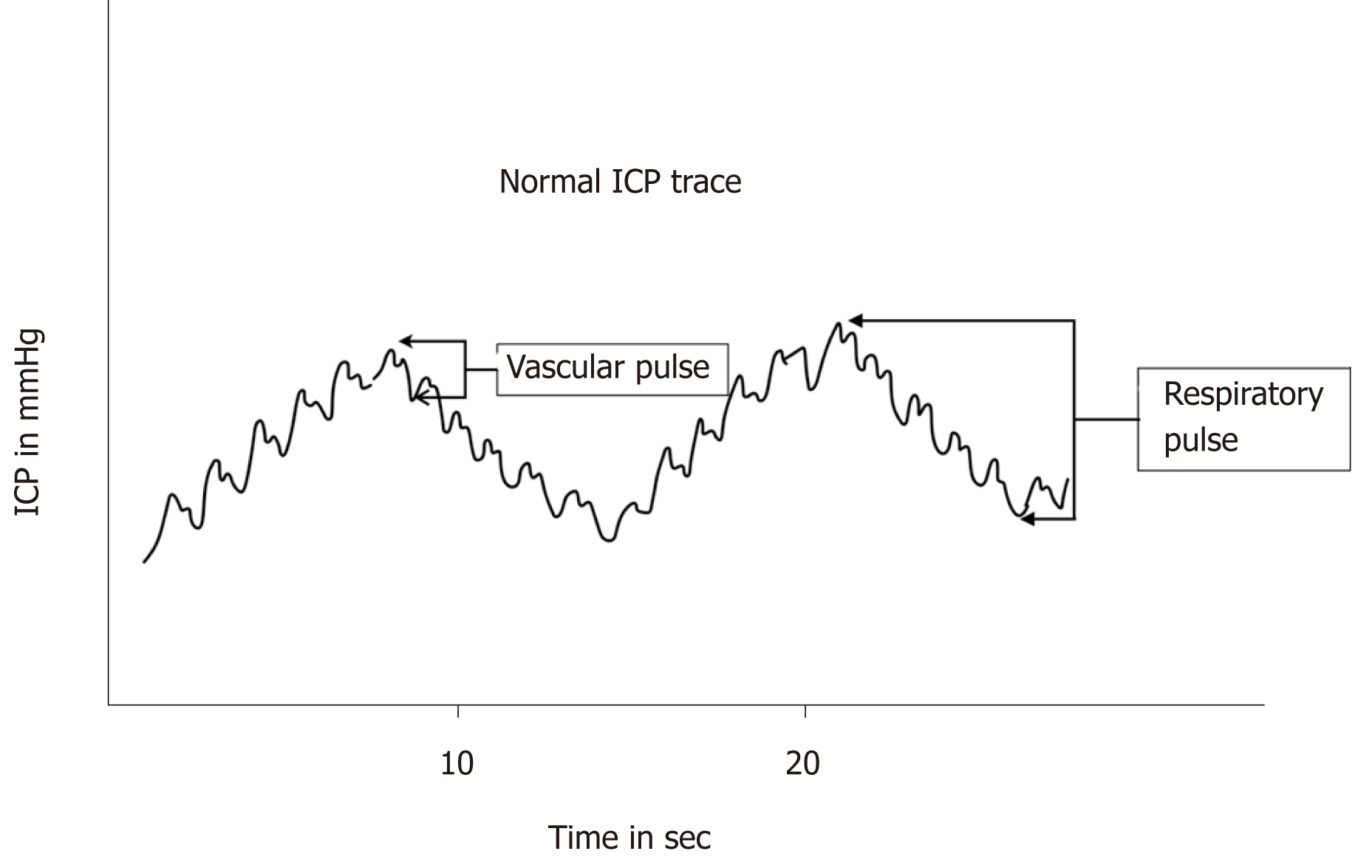
The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the icp stable with csf pressures varying by about 1 mmhg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of csf. Changes in icp are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained. Changes in icp waveform.
The normal level of mean intracranial pressure icp in a resting healthy adult in the horizontal position is 7 10 mm hg. They are frequently accompanied by neurological deterioration. In a healthy adult the icp is usually in the range of 0 to 10 mmhg and any pressure greater than 20mmhg is abnormal.
Normal icp ranges from 5 15mmhg. Increased icp in infants can be the result of injury such as falling off a bed or it can be a sign of child abuse known as shaken baby syndrome a condition in which a small child has been. The data on the usefulness of routine icp monitoring in severe head injury is controversial.
Icp is measured in millimeters of mercury and at rest is normally 7 15 mmhg for a supine adult. A waves or plateau waves these comprise a steep rise in icp from near normal values to 50 mm hg or more persisting for 5 20 minutes and then falling sharply. These waves are always pathological and indicate greatly reduced compliance.
The normal icp is pulsatile and reflects the cardiac and respiratory cycles fourier analyses give three different slow waveforms. An icp 15 mm hg is considered pathological although this varies with the condition. Intracranial pressure can increase to as high as 70 cm h 2 o normal 20 cm h 2 o during the first and second stages of labor.
 Mean Upper Limit Of Normal Intracranial Pressure Derived From Studies Download Table
Mean Upper Limit Of Normal Intracranial Pressure Derived From Studies Download Table
 Increased Intracranial Pressure Ppt Video Online Download
Increased Intracranial Pressure Ppt Video Online Download
 Monitoring And Interpretation Of Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Monitoring And Interpretation Of Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
 Intracranial Pressure Measurement
Intracranial Pressure Measurement
Revista Brasileira De Terapia Intensiva
New Therapies For Intracranial Hypertension
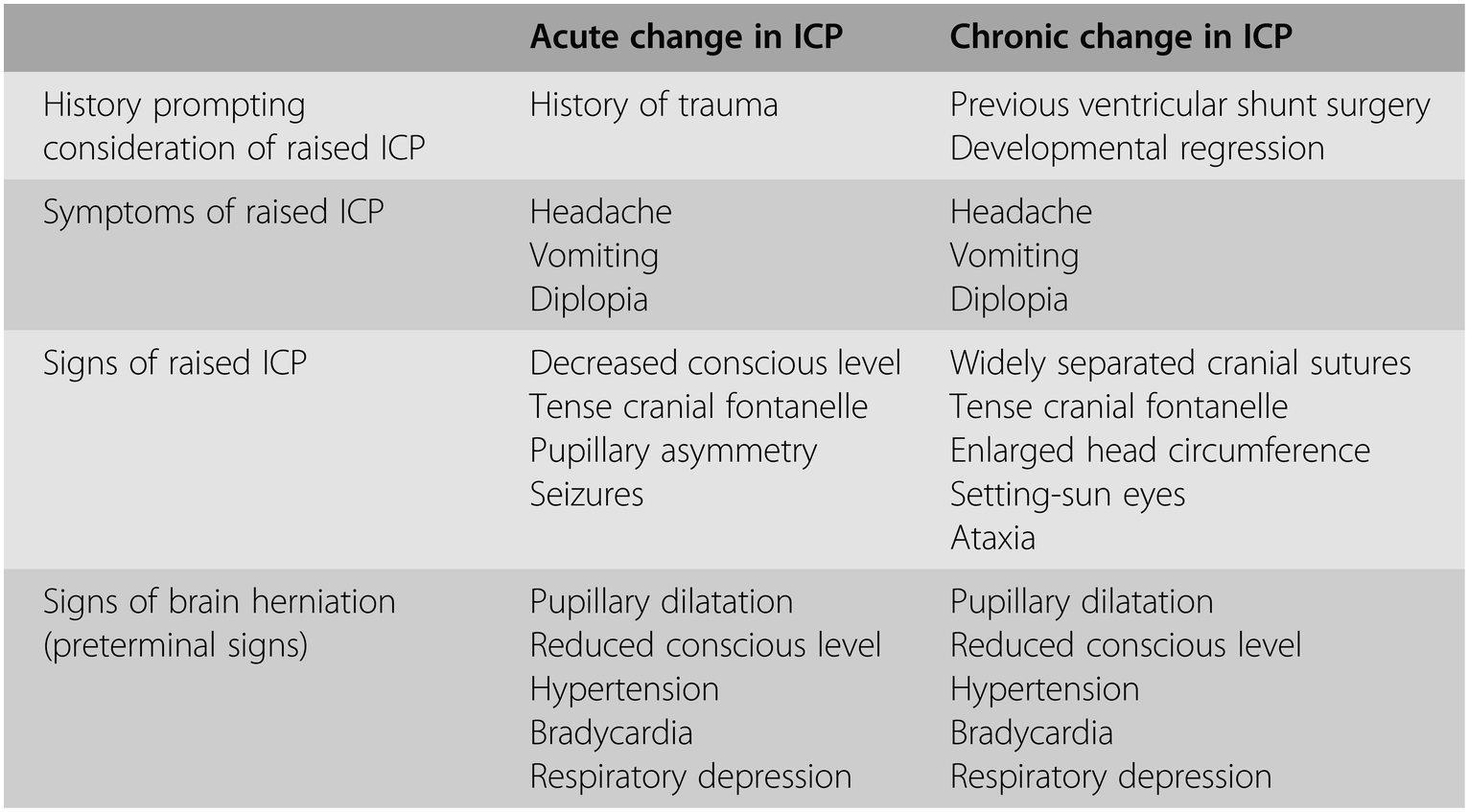 The Child With Raised Intracranial Pressure Chapter 19 Managing The Critically Ill Child
The Child With Raised Intracranial Pressure Chapter 19 Managing The Critically Ill Child
 Intracranial Pressure Measurement
Intracranial Pressure Measurement
 Monitoring And Interpretation Of Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Monitoring And Interpretation Of Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
 Mean Upper Limit Of Normal Intracranial Pressure Derived From Studies Download Table
Mean Upper Limit Of Normal Intracranial Pressure Derived From Studies Download Table
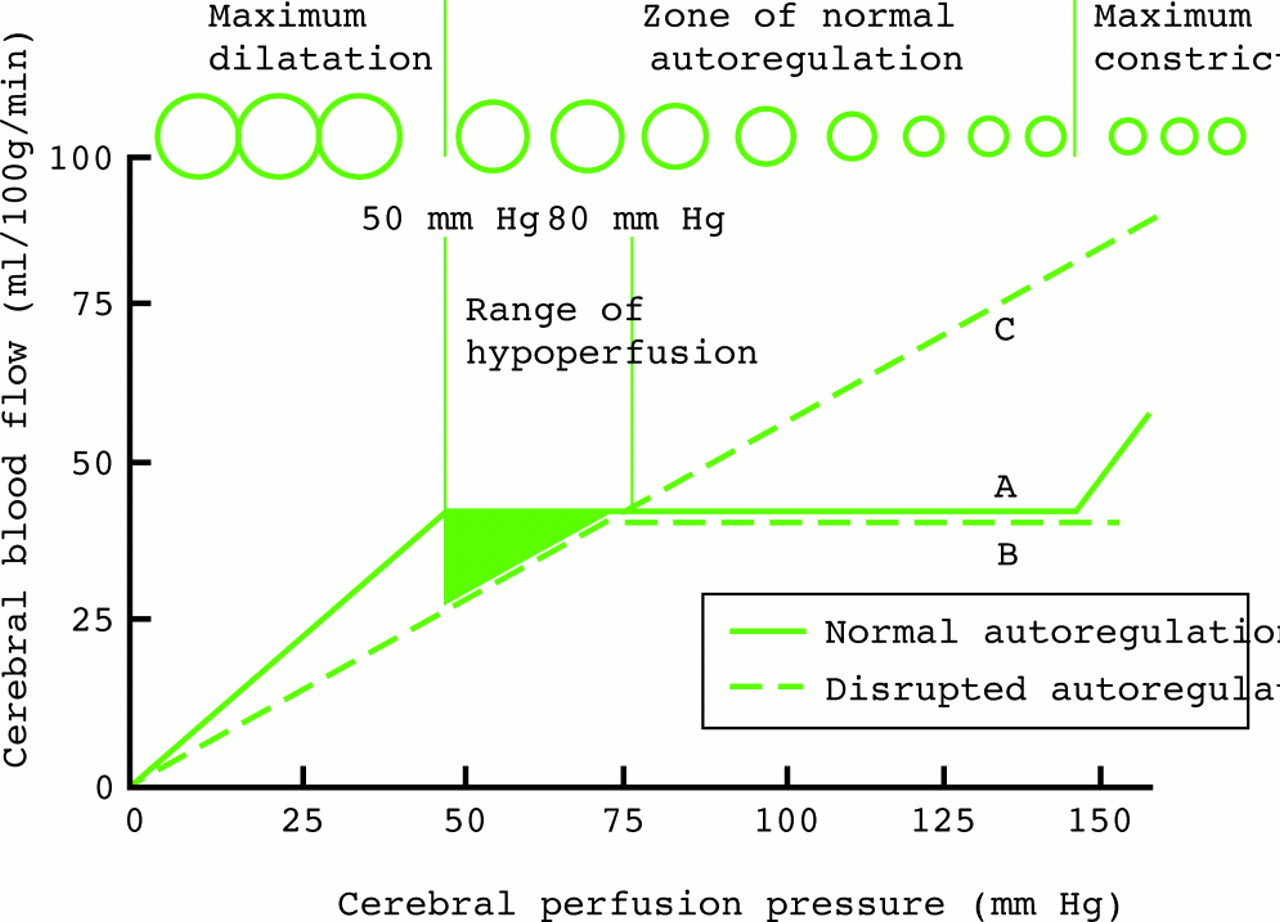 Raised Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Raised Intracranial Pressure Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
New Therapies For Intracranial Hypertension
 Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Gold Standard And Recent Innovations
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Gold Standard And Recent Innovations
